Forests constitute an important natural resource of the state, which provides timber, fuel, fodder, wood, timber, herbs, house construction, packaging of the horticultural produce and in agricultural implements, medicinal plants, etc.
The forests contribute 1/3 of the total revenue of the state and also provide employment to a sizable population. Distribution of various species is fairly according to regular altitudinal stratification except where the micro-climate changes due to aspect, exposure, and local changes in the rock and soil bring in vegetation inversion.
Out of the total of 45,000 species of plants found in India, 3,295 species are in this state.
Based on legal classification the forests of the state can be classified as reserved, demarcated, unprotected demarcated, un-classed forests.
According to physiographic and district-wise location and dominant tree types Forests Regions of Himachal can be classified into four types as follows:
| Forest Regions | Physiographic Location | District Wise Location | Major Forest Types |
| Sub-montane or Subtropical | Southernmost tract of the state – Shiwalik hills, dun valleys & foothills of lower Himalaya. | Parts of Chamba, Kangra, Mandi, Bilaspur, Solan, and Sirmaur | Sal, riverine Khair & Sisham, Chir Pine, Dry Deciduous & Lower Moist Broad Leaved Forest |
| Montane or Temperate Region | Upper hills of the lower Himalaya, Middle Himalaya & lower tracts of Higher Himalaya. | Parts of Chamba, Kangra, Bilaspur, Mandi, Kullu, Shimla, Solan, Sirmaur, Kinnaur. | Ban,Kharsu and Moru Oak, Deodar, Blue Pine, Fir, Spruce, Chir Pine & Mixed Broad Leaved Forest. |
| Sub-Alpine and Alpine Regions | Upper slopes of Lower & Middle Himalaya, Higher Himalaya & south facing lower slopes of the TransHimalaya. | Parts of Chamba, Kangra, Lahaul & Spiti, Kullu, Shimla, Kinnaur. | High-Level Blue Pine, Fir, Spruce, Alder, Birch & Rhododendron Forest & Moist Alpine scrub. |
| Trans Himalayan Region | Inner dry valleys of the main Himalaya & Trans-Himalaya. | Parts of Chamba, Lahaul & Spiti, Kullu, Shimla, Kinnaur. | Chilgoza or Neoza pine forest, Dry Deodar, Juniper & Alpine scrub. |
The major trees, shrubs, and herbs of Himachal are as follows:
Trees found in Himachal Pradesh: Akoria (Rhus), Akash bel (Cusevta refles), Akrot (vugulans regia), Amaltas (Cassia fistula), Bargad (Ficus benghalensis), Chil (Pinus longifolia), Haldia (Adina cardilolia), Harar (Terminalia chebule), Kachnar (Bauhinia variegate), Kakare (Pistacia integerrime), Semal (Salmalia malabarica), Simbal (Bombax malabaricum, Seriphal (Acgle marmelos) and kaiphal (Myrica nagi) beside several other trees like varios species of pines, fodder trees, acacia spp. etc.
Shrubs: Bhatindu (Cissampelos pareira), Dhai (Woodfordia fncticosa), Kamal (Man philippinensis) Kural (Medua helix), Thuna (Taxus baccata) and Tut (Morus alba).
Herbs: Bhang (Cannabis sativa), Ritha (Sapindus trifoliayus), Toon (Toona ciliate), Mehndu (Dodonaca viscas) and Tunga (Rhus cotinus).
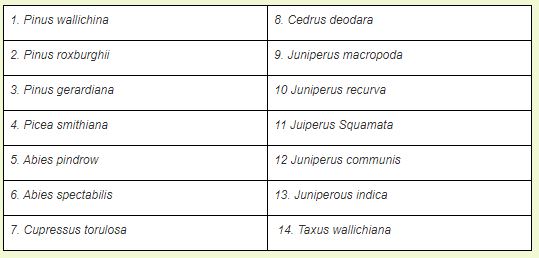
Major Timber Resources of Himachal Pradesh are Conifers viz. Cedrus deodara, Pinus roxburghi: P wallichiana Picea smithiana Abies pindrow A spectabilis Cupressus torulosa, Juniperus excelsa and J. sequamata. Broad leaved species viz. Shorea robusta, Quercus leucotricophora, Q. floribunda, Q. dilatata, Aesculus indica, Acer spp., Juglans regia, Acacia catechu, Dalbergia sissoo, Toona ciliata, Alnus nepalensis etc.
Fodder And Fuel Wood Yielding Species: Grewia optiva, Morus alba, Bauhinia variegata, Celtis australis, bamboos, Albizia chinensis, A. lebbeck and Robinia pseudocacia.
Non Wood Forest Resources like grasses, fruits, leaves, bark, animal products, bamboo, canes, grasses fibers, flosses, essential oils, fixed oils, waxes, dyes and tans, medicinal plants, gums and resins, drug yield specifies, poisons, insecticides and miscellaneous forest produce (lac, honey, tandu leaves).
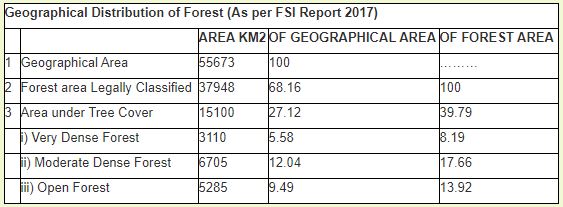
Geographical distribution of Forests in Himachal Pradesh:
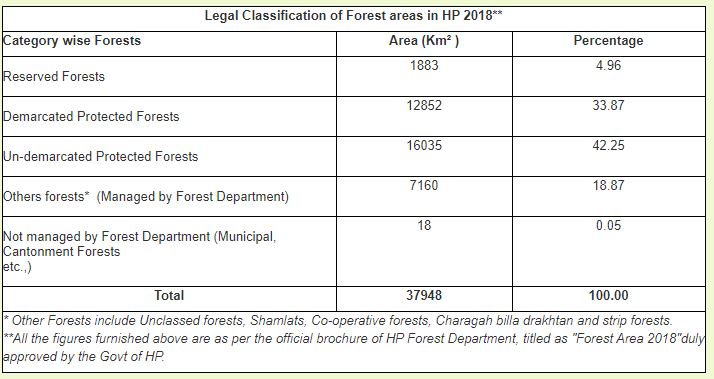
Legal Classification of Forest areas in HP 2018:
Conifers Found in Himachal:
Forest cover and vegetation cover are both same
Scientific names of many flora species are wrong