Tax base collection
Revenue comprises all the receipts of the government from taxes, custom duties, revenue from state-owned enterprises, capital revenues, and foreign aid. As per the HP budget estimates, the revenue receipts of the government for the year 2020-21 were estimated to be 24.56 % of the GSDP which were 19.86% in 2019-20 estimates. Government receipts can be divided into non-debt and debt receipts.
Non-debt revenue receipts-
- Tax revenue
- Non-tax revenue
- Recovery of loan
- Disinvestment
Debt revenue receipts-
- Market borrowing
- Other liabilities
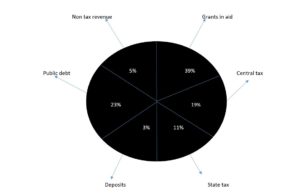
Rupee come from (2021-22)
| CATEGORY | 2019-20(RE) | 2020-21(BE) |
| Tax revenue | 7.79% | 9.81% |
| Non tax revenue | 1.46% | 1.54% |
| Revenue receipts | 19.86% | 24.56% |
Tax revenue-
- It is the income gained by the government through direct taxation.
- Example- Income tax, wealth tax, corporation tax and property tax etc.
- According to HP budget estimates of 2020-21, tax revenue was estimated at Rs.15356 crore as against Rs.12682 crore in 2019-20. Tax revenue was contributed 7.79% to GSDP in 2019-20.
Non tax revenue-
- It is the income gained by the government through indirect taxation.
- It consists of interest receipts on loans, dividends and profit from public sector undertaking and receipts from services provided by the government like general services such as services provided by the public service commission, social services such as health, education, economic services such as irrigation etc.
- According to HP budget estimates of 2020-21, non-tax revenue was estimated at Rs.2410 crore as against Rs.2372 crore and contributed 1.46% to GSDP in 2019-2020.
Public debt-
- Sources of public debt are dated government securities (G-Secs), external assistance, and short-term borrowings.
Grants in aid-
- Grants-in-aid are given by the Union Government to State Governments /Panchayati Raj Example – statutory grant, discretionary grant etc.
Why tax base collection less in HP-
- Approx 89% HP population lives in rural areas and they do agriculture, animal husbandry, horticulture etc. and India does not tax income from agriculture.
- Apart from rural workers many wealthy landowners/ business person are out of tax ambit because they claim their income as earned from agriculture.
- Less industries and infrastructure project exist in HP as compared to other states which lead to getting less collection of corporate tax.
- More than 50% of HP population is out of tax ambit or various other exemption offered to senior citizens.
Pros and Cons of special category status-
‘Special category’ status is given by the centre government to assist in development of those states that face geographical & socio-economic constraints like hilly terrains, economic & infrastructural backwardness and non-viable state finances.
‘Special category’ status came into play in 1969 recommended by the 5th finance commission in order to share the funds of central government among all states. As per NITI Aayog report 11 states namely, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura and Uttarakhand were granted special category status.
Criteria of special category status-
States must having certain characteristics to get special category status based on the recommendation of the national development council.
- Hilly terrain
- Economic backwardness
- Poor infrastructure
- Strategic location along borders with neighboring countries
- Low population density
- Larger share of tribal population.
- Non-viable nature of state finances
Pros of special category status-
- Concession on excise duty to attract industries in the state.
- The central government bears 90% of the state expenditure on all centrally sponsored schemes and rest 10% is given as loan to state at zero percent rate of interest.
- States with special category states (SCS) are exempted from custom duty, income tax, corporate tax to attract investment.
- A huge 30% amount of planned expenditure of the central budget goes to ‘Special Category’ States.
- Special Category States can avail the benefit of debt relief schemes.
- Unspent money does not lapse and get carry forward for the next financial year.
Issue with special category status-
- Criteria to determine special category status has been a matter of debate because various committees used different parameters to classify state in special category.
- Some states lobby central government to classify them in special category. For instance-Bihar, Madhya Pradesh
- Committee reports, data shows that state with special category states not much economic progress has been noticed.
- After 14th finance commission, tax devolution to states increased from 32% to 42%. Thus it has been reduced central assistance to special category states.
Read also:
- Gorkha invasion- its nature and consequences, Treaty of Segauli.
- Emergence and growth of early medieval states: Kangra, Kullu, and Chamba. The Hill States and their relations with the Mughals and the Sikhs
- Growth of Industrial areas and types of Industries in Himachal Pradesh
- Tribal welfare administration, Tribal sub-plan, and Single-line administration in Himachal Pradesh
- Medicinal and Aromatic plants resources of the State of Himachal Pradesh