Revenue comprises all the receipts of the government from taxes, customs duties, revenue from state-owned enterprises, capital revenues, and foreign aid. As per the HP, budget estimates the revenue receipts of the government for the year 2020-21 were estimated to be 24.56 % of the GSDP which were 19.86% in 2019-20 estimates. Government receipts can be divided into non-debt and debt receipts.
Non-debt revenue receipts-
- Tax revenue
- Non-tax revenue
- Recovery of loan
- Disinvestment
Debt revenue receipts-
- Market borrowing
- Other liabilities
Tax revenue– is the income gained by the government through direct taxation. Example- Income tax, wealth tax, corporation tax, and property tax, etc. According to HP budget estimates of 2020-21, tax revenue was estimated at Rs.15356 crore as against Rs.12682 crore in 2019-20. Tax revenue was contributed 7.79% to GSDP in 2019-20.
Non-tax revenue- is the income gained by the government through indirect taxation. It consists of interest receipts on loans, dividends, and profit from public sector undertaking and receipts from services provided by the government like general services such as services provided by the public service commission, social services such as health, education, economic services such as irrigation, etc.
According to HP budget estimates of 2020-21, non-tax revenue was estimated at Rs.2410 crore as against Rs.2372 crore and contributed 1.46% to GSDP in 2019-2020.
Non-debt capital receipts- consist of recovery of loans, advances, and disinvestment receipts. The HP budget estimate for 2020-21 envisages Rs.26 crore as a recovery of loans and no income from disinvestment.
| Category | 2019- 20(RE) | 2020-21(BE) |
| Tax revenue | 7.79% | 9.81% |
| Non-tax revenue | 1.46% | 1.54% |
Tax as a percent of GSDP
Revenue generation from tourism
HP is a major tourism destination and contributes to a state GDP is about 7% which is quite significant. HP has lots of prospects of tourism which are following.
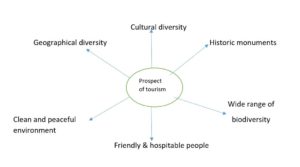
Tourism is a multidimensional industry having an interface with several other sectors of the economy. Therefore it is an accelerator of the overall economic development of the state.
Employment generation-
- Tourism sector is able to generate employment by two means: directly and indirectly
- Directly through restaurants, hotel, nightclubs, taxis etc.
- Indirectly through the supply of goods and services needed by the tourism-related businesses.
- By providing employment, it generates revenue to the government.
Foreign exchange earnings-
- As of December 2019, foreign tourist arrival reached 383000 in HP.
- Tourism expenditure generates income for the host economy and can stimulate the investment necessary to finance growth in other economies’ sectors.
- International tourism is the main source of generating foreign exchange earnings.
Contribution to local economies-
- Domestic tourist inflow in the state reached 16.83 million in 2019.
- Money is earned from tourism through informal employment eg- street vendor guides, rickshaw drivers.
- The main advantage of informal employment is that the money is returned to the local economy and has a great multiplier effect as it is spent over and over again.
Infrastructure development-
- Tourism can induce the local government to make infrastructure improvements such as better water and sewage system, roads, electricity, telephone, and public transport network.
- They can improve the quality of life for residents as well as facilitate tourism.
Government revenues-
- Direct contributions are generated by taxes on income from tourism employment and tourism businesses and by direct levies on tourists such as departure taxes.
- Indirect contributions come from taxes and duties levied on goods and services supplied to tourists.
Revenue generation from hydro potential
Hydropower is a renewable source of energy along with cheaper as compared to electricity generated from coal and gas-fired plants. HP has immense potential for hydropower as it is naturally blessed with abundant streams and rivers flowing down from mountains. The state of HP has an estimated hydro potential of 27,436MW out of which 24000MW has been assessed.
Hydropower development is the key engine to the economic growth of the state of HP as it makes a direct and significant contribution to the economy in terms of revenue generation, employment opportunities, and enhancing the quality of life.
Revenue generation-
- Hydropower is the major source of income of the HP government.
- Revenue received from sale of HP government share of power up to 31st December 2020 is Rs.610 crore whereas budget estimates Rs.900 crore for financial year 2020-21.
- Nathpa Jhakri project (Shimla), Girinagar hydel project (Sirmour), Sanjay vidyut project (Kinnaur), Bassi hydroelectric project (Mandi) are the major project which generate both electricity and revenue to HP government.
- HP has supplied electricity to its neighborhood state. Example– Renuka project on Yamuna River in HP provide supply of electricity to Haryana, Delhi, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan.
Employment generation-
- The Union Cabinet approved a proposal for an expenditure of Rs.1810 crore (US$ 245.41 million) for the 210 MW Luhri Stage-I hydropower project in Himachal Pradesh on the Satluj River.
- The project will help create approx.2000 direct and indirect jobs and will contribute to the state’s overall socioeconomic growth
- It creates a variety of recreational opportunities such as fishing, swimming, rafting, boating
Infrastructure development
- Hydroelectric installations bring electricity, highways, industry, and commerce to communities, thus developing the economy, expanding access to health and education, and improving the quality of life.
Revenue generation from flora and fauna-
The term flora relates to all plant life and the term fauna represents all animal life. In Himachal Pradesh, there is a dynamic relationship between common property resources (CPR) such as forests, water, livestock, crops, and grazing land. Both Flora and fauna are integral to the sustainability of the economy of HP.
Fauna-
The livestock sector of India’s economy is the largest in the world with 537.5 million in population and contributes 4.11% to the GDP of the country.
Himachal Pradesh has vast resources of livestock because 89.97% population of HP lives in the villages of rural areas. According to the 20th livestock census 2019, cattle, buffaloes, goats, sheep, horses are the major livestock of HP. The livestock provides food and non-food items to the people which are following.
Food Security-
- The rearing of livestock is an integral component of the rural economy.
- The livestock provides food items such as Milk, Meat, fish and eggs are an important source of protein for human consumption.
- The contribution of major livestock products during the year 2019-20.
| Category | Production |
| MILK | 15.31 (lakh ton) |
| WOOL | 1516 ton |
| EGG | 106.62 (million ton) |
| MEAT | 4601 ton |
- As a result, the sector plays a significant role in reducing poverty, combating food insecurity and malnutrition.
Employment generation-
- Animal husbandry comprises mainly small and marginal farmers, less literate and agro-pastoralists, etc.
- Livestock including the sale of milk, poultry, wool procurement of sheep and angora, aquaculture, and other animal product create cash for rural people.
- 70% of those employed in the sector are women.
- It can also provide employment opportunities such as transport of produce, fuel, as well as inputs for crop production.
Income-
- Animal products including sheep meat, goat meat, poultry products, animal casings, milk and dairy products, fish, honey, leather are the most important product which has very high export potential.
- The animals also serve as moving banks and assets which provide economic security to the owners. Example Gaddi tribe -shepherds of HP.
- Livestock such as sheep, goats, horses, and mules serve as income during emergencies to meet the expenditures like marriage, children education, construction of houses, treatment of a sick person, etc.
Dung-
- Animal dung (cow, buffalo ox) is used for several purposes which include dung cakes, fertilizer, and useful building material, etc.
- Dung may be used to produce biogas to generate electricity and heat.
- Cow dung is the main input of natural and organic farming to increase soil carbon, reduce soil erosion, runoff, and nitrate leaching.
FLORA-
Flora means the plant naturally occurring in a particular area. It includes forests, flowering, and non-flowering plants, grasslands, trees, etc.
Forests in Himachal Pradesh cover an area of 37948 sq. km and account for 68.16% of the total geographical area of the state.
HP has vast resources of medicinal, herbs, aromatic plants, etc.
Medicinal and herbs plants in HP – Isabgol, Ashwagandha, Long pepper, Amla, Acacia catechu, Bhringhraj, Safeda, Kulth, etc.
Aromatic plant in HP – Mint, Lemongrass, Geranium, Coriander, etc.
Employment-
- Forest activities create jobs including nursery operation, tree planting, timber cruising, and logging, etc.
- Medicinal plant in HP also has the potential to provide employment to a large number of people through nursery raising, medicinal and aromatic farming, and entrepreneurship development for nursery trade, value addition, and export.
Income-
- During 2017-18, the value of timber product services is about 0.31% of HP state GDP.
- During 2017-18, the value of Non-timber forests products (resin, turpentine oil, bamboo, medicinal plant, fungi, etc.) is about 0.27% of HP state GDP.
- Rural households in HP collect food, fuel, medicinal plant, timber, shrubs, etc., and generate cash incomes by selling such material.
Food Security-
- A wide range of trees and forest products regularly provide food for people or fodder for their livestock.
- Flora also provides essential ecosystem services that support sustainable agriculture by maintaining soil fertility, stabilizing soils, regulating water flows, and providing a viable habitat for wild pollinators and predators of agricultural pests.
Read also:
- Concept of Eco-Tourism and green tourism and their role in the sustainable development of the State of Himachal Pradesh – HPAS Mains
- Himachal Pradesh Industrial Investment Policy, 2019 – HPAS Mains
- Environmental concerns of the tourism industry, both positive and negative effects including climate change with reference to Himachal Pradesh – HPAS Mains
- Concept of Himachal State Wide Area Network (HIMSWAN) – HPAS Mains
- Concept of LokMitra Kendra in Himachal Pradesh – HPAS Mains
- What is Mukhya Mantri Seva Sankalp Helpline?
- Aryabhatta Geo-Informatics Space Application Centre (AGISAC) – HPAS Mains
- Kangra Tea – Himachal Pradesh
- Relevance and role of Intellectual Property Rights, Geographical Indications and Traditional wisdom and knowledge in the sustainable development of the State